Accounting Equation Basics, Example and Formula
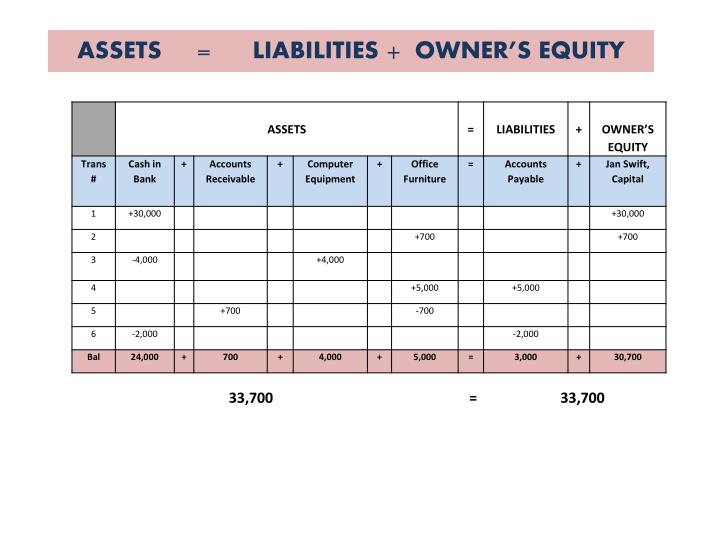
In the below-given figure, we have shown the calculation of the balance sheet. Being an inherently negative term, Michael is not thrilled with this description. Our easy online application is free, and no special documentation is required. All participants must be at least 18 years of age, proficient in English, and committed to learning and engaging with fellow participants throughout the program.
What Is the Accounting Equation?

The main limitation of the Accounting Equation is that it doesn’t tell us anything about the company. The formula is more of a principle than a metric that yields significant insight. It tells us that Assets must equal Liabilities and Equity. Said differently, it states whatever value of Assets left after covering Liabilities is entitled to Equity holders. It doesn’t tell us anything unique about any specific business. It doesn’t tell us how the business is performing, whether its financial health, or how much the company is worth.
Accounting Equation Outline
That part of the accounting system which contains the balance sheet and income statement accounts used for recording transactions. A company’s liabilities include every debt it has incurred. These may include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred journal entry for loss of insured goods assets revenues, bond issues, warranties, and accrued expenses. Anushka will record revenue (income) of $400 for the sale made. A trade receivable (asset) will be recorded to represent Anushka’s right to receive $400 of cash from the customer in the future.
The Language of Business
Regardless of the size of a company or industry in which it operates, there are many benefits of reading, analyzing, and understanding its balance sheet. Retained earnings are the net earnings a company either reinvests in the business or uses to pay off debt. The remaining amount is distributed to shareholders in the form of dividends.
If a company wants to manufacture a car part, they will need to purchase machine X that costs $1000. It borrows $400 from the bank and spends another $600 in order to purchase the machine. Its assets are now worth $1000, which is the sum of its liabilities ($400) and equity ($600). This transaction affects both sides of the accounting equation; both the left and right sides of the equation increase by +$250.
Put another way, it is the amount that would remain if the company liquidated all of its assets and paid off all of its debts. The remainder is the shareholders’ equity, which would be returned to them. The accounting equation is also called the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation.
- As noted above, you can find information about assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity on a company’s balance sheet.
- Public companies, on the other hand, are required to obtain external audits by public accountants, and must also ensure that their books are kept to a much higher standard.
- A company will be able to quickly assess whether it has borrowed too much money, whether the assets it owns are not liquid enough, or whether it has enough cash on hand to meet current demands.
- If you take the total value of Assets and subtract the total value of Liabilities, then the remainder is value for Equity holders.
- $10,000 is debited to cash, and $10,000 is credited to equity because it’s owed to Jim.$30,000 is also debited to cash, and $30,000 is credited to liabilities because it’s owed to the bank.
If an accounting equation does not balance, it means that the accounting transactions are not properly recorded. To calculate the accounting equation, we first need to work out the amounts of each asset, liability, and equity in Laura’s business. The accounting equation shows the amount of resources available to a business on the left side (Assets) and those who have a claim on those resources on the right side (Liabilities + Equity).
The system is the go-to accounting method of the modern day. And Accounting Equation is the premise on which the double-entry accounting system is built. The Accounting Equation states that the total value of a company’s Assets must equal the total value of its Liabilities and Equity. Because you make purchases with debt or capital, both sides of the equation must equal. If the balance sheet you’re working on does not balance, it’s an indication that there’s a problem with one or more of the accounting entries.
Taking time to learn the accounting equation and to recognise the dual aspect of every transaction will help you to understand the fundamentals of accounting. Whatever happens, the transaction will always result in the accounting equation balancing. The inventory (asset) of the business will increase by the $2,500 cost of the inventory and a trade payable (liability) will be recorded to represent the amount now owed to the supplier. Sole proprietors hold all of the ownership in the company. If your business has more than one owner, you split your equity among all the owners.
If splitting your payment into 2 transactions, a minimum payment of $350 is required for the first transaction. Together, these line items make up total shareholders’ equity. Everything listed is an item that the company has control over and can use to run the business. In Double-Entry Accounting, there are at least two sides to every financial transaction.




